Meet American Empire’s ‘Doctor Death’
In the 1962 film adaptation of Richard Condon’s The Manchurian Candidate, a diabolical North Korean doctor named Yen Lo tells Staff Sergeant Raymond Shaw to “pass the time with a little solitaire.” These trigger words, accompanied by a Queen of Diamonds playing card, prompts the lanky soldier to get up, and when instructed, brutally kill two of his own comrades sitting on the stage, both of whom appear under the same trance as Raymond.
Later, we find out this was not a dream but a real test of Shaw’s programming through elaborate mind control, undertaken before he is sent home to the United States as a sleeper agent for a Communist Party cell, led by his own mother. “His brain has not only been washed, as they say, but cleaned,” declares a gleeful Dr. Lo.

The film was released when the country was in a state of high Cold War anxiety. The idea that the Communists were deep into finding a way to brainwash and program individuals to deploy as weapons of war was not new, of course. It was just finding its way into the increasingly paranoid popular culture. But what Americans did not know was that our own government was in part responsible for those stories as a cover for their own brainwashing experiments, which were racing along at the speed of a freight train.
In 1953, Allen Dulles told a group of fellow Princeton alumni that the U.S. was far behind the Russians and North Koreans in “brain warfare.” He warned of a mind control gap that would likely grow because “we in the West..have no human guinea pigs to try these extraordinary techniques.”
This was a lie of breathtaking proportions. For several years, his CIA had already been conducting extreme experiments on unwitting “human guinea pigs” at black sites in France, Germany, and South Korea. Shortly after he broadcast this cynical lament to the Princeton lads, he approved MK-ULTRA, the most illicit and morally corrupt intelligence program in American history (that we know of). In it, the CIA tested a stomach roiling variety of unregulated drugs, electro-shock, sensory deprivation, and other extreme techniques on unwitting souls across the United States—in “safe houses,” prisons, psychiatric hospitals, doctors’ offices—even in the CIA itself. People died, went crazy, or withered away in a vegetative state, often with little or no clue of what had happened to them.
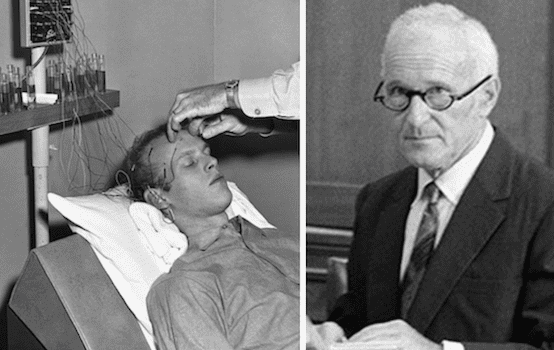
In Poisoner in Chief, released today, journalist and author Stephen Kinzer makes Dr. Sidney Gottlieb the manifestation of the U.S. government’s Cold War obsession with winning, its warped moral compass, and its utter disregard for the law. From 1951 to the late 1960s, under Dulles’ protection, Gottlieb was the principal player in what can only be called a maniacal mission to find the perfect drug to destroy/control/reprogram the human mind (he believed, though he was never able to prove, that the drug was LSD).
Gottlieb was also the chief scientist in a CIA program that developed poisons with which to assassinate world leaders (failed attempts included Cuba’s Fidel Castro and Congolese Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba), tested aerosol-delivered germs and deadly gases, and honed extreme torture techniques. He’s been called Dr. Death, Washington’s “official poisoner,” and a mad scientist. But “Sidney Gottlieb” never became a household name, mostly because he never paid for his crimes. Thanks to Deep State politics, statutes of limitations, a great lawyer, and depressingly weak congressional investigators, Gottlieb was able to take the worst of his secrets to the grave in 1999.
Now, pulling together a trove of existing research, newly unearthed documents, and fresh interviews, Kinzer puts the fetid corpus of American Empire back under a microscope. It isn’t pretty—but it is instructive.
“Commitment to a cause provides the ultimate justification for immoral acts. Patriotism is the most seductive of those causes,” Kinzer surmises in an attempt to give context to Gottlieb and Dulles, and Gottlieb’s closest patron and conspirator, Richard Helms, who served as CIA chief after Dulles and during the later years of MK-ULTRA.
“Some do things they know are wrong for what they consider good reasons,” Kinzer continued. “No one else of Gottlieb’s generation, however, had the government-given power to do so many things that were so profoundly and horrifically wrong. No other American—at least, none that we know of—ever wielded such terrifying life-or-death power while remaining so completely invisible.”
With so much material to work with, Poisoner in Chief is a parade of outrages. But by the time the twisted calliope falls silent, two major themes are left to contemplate.
First, Gottlieb did not emerge in a vacuum but in the primordial ooze of moral justification following World War II. While America was putting its public virtue on display during the Nuremberg trials, the army under the Joint Intelligence Objectives Agency was courting Nazi scientists who had been involved in the most grotesque human experimentation imaginable during the war. Their expertise in biological warfare and psychoactive drugs was highly prized. The Americans had to make sure, after all, that the commies didn’t get to them first.
So under Operation Paperclip, the army “bleached” their records and brought these men in among several hundred other scientists, engineers, and technicians who served the Third Reich. Instead of prison, they were settled into comfortable obscurity in suburban Washington, working for the U.S. government.
For those whose crimes were not so easily scrubbed, the army found ways to collaborate with them overseas in even less controlled environs. Like Kurt Blome, a Nazi scientist who deliberately infected prisoners with deadly viruses, including the plague, at the Auschwitz concentration camp and other sites. After saving him from the gallows at Nuremburg, officials quietly installed him in the European Command Intelligence Center at Oberursel, West Germany—otherwise known as “Camp King”—to conduct more experiments, but on our side.
The same went for Japanese scientist Shiro Ishi, who was reportedly responsible for some 10,000 deaths in and around his Manchurian complex called Unit 731 during the war. His ghastly activities included everything from slow-roasting test subjects with electricity, to amputating limbs and dissecting people alive to monitor their slow deaths. At one point, he lined up naked Chinese women and children to see how long they would live after being struck by shrapnel in the buttocks. He also created tons of anthrax that was later used to kill thousands of Chinese civilians.
But instead of bringing this monster to justice, U.S. agents granted Ishi and his Japanese collaborators immunity and obtained all of his research on how toxins affect the body—including all of the tissue slides from people whose organs were taken out while they were still alive. “Scientists at Camp Detrick (Maryland) were delighted,” Kinzer writes.
“Thus did the man responsible for directing the dissection of thousands of living prisoners…escape punishment,” he adds, noting that Ishi and his minions were deployed to U.S. detention centers in East Asia, where they “helped Americans conceive and carry out experiments on human subjects that could not legally be conducted in the United States.
Secondly, Kinzer highlights how easily American government officials adopted their former wartime foes’ detached, ruthless approach to human experimentation, embarking without guidance or oversight on what appears to be a fanatical quest without consequences. At a time when many Americans were zooming to suburbia in search of “Leave it to Beaver,” Gottlieb was hiring people like George White, straight out of “The Sweet Smell of Success.”
White was “a hard charging narcotics detective who lived large in the twilight world of crime and drugs” writes Kinzer. In 1953 he started setting up “safe houses” in New York and San Francisco where he would use pay hoodlums and prostitutes in drugs and dough to dose unsuspecting subjects with increasing amounts of LSD at “parties” while the CIA peeped the action from two-way mirrors outfitted with cameras.
Meanwhile, Gottlieb gave tons of cash and LSD to doctors like Harris Isbell at the Addiction Research Center in Lexington, Kentucky. “Officially this center was a hospital, but it functioned more like a prison,” writes Kizner. “Most inmates were African American from the margins of society. They were unlikely to complain if abused.”
And abused they were, like most of the test subjects at the prison programs financed by the CIA. If they were told they were part of a test (agreement was typically in exchange for something, like good behavior credits or high grade heroin), they weren’t told what kind of drugs they were given or how much. Many of the experiments involved dosing subjects with greater and greater amounts of LSD over long periods of time. Gottlieb wanted to see at what point the mind would dissolve. “He was pleased to have secured a supply of ‘expendables’ across the United States,” Kinzer notes.
Certainly his test subjects at the CIA interrogation cites overseas were “expendable.” Kinzer offers a number of cases in which foreign detainees, usually suspected spies, were given massive amounts of different drugs “to see if their minds could be altered.” Others were given electro shock. They were later killed, “and their bodies burned.”
Then there were the seemingly random tragedies. Like art student Stanley Glickman who was believed to be drugged directly by Gottlieb while at a Paris cafe in 1952, and then taken into a hospital where more “testing” occurred. It was the end of “his productive life,” writes Kinzer. Glickman died alone and mentally ill in New York city several decades later. Or Frank Olson, a CIA scientist who “fell or jumped” from a Manhattan hotel window after being unwittingly dosed at a “retreat” hosted by Gottlieb a week earlier. Though his family tried, they were never able to pin his strange death on Gottlieb or the government.

Kinzer shows that sometimes paranoia comes from a very real place—that Big Brother was not only watching, but for nearly 20 years he was drugging and testing germs and other toxins on unsuspecting Americans like they were laboratory animals. And Gottlieb, Dulles, and Helms were no fictional spawn of an over-active imagination. They were highly respected and powerful men with a combined 105 years of government service. They were the system.
So how do we digest this today? We can start by acknowledging that the ends will always justify the means because the government always gets away with it. And we are still living with the effects. The torture techniques set into motion in the 1950’s, for example, later surfaced in the dark corners of the Phoenix Program in Vietnam, and more recently in the dirty cells of Abu Ghraib detention center.
Indeed, with a head full of Red Menace and lord knows what else, these so-called stalwart men of the “Greatest Generation” pounded the earth as though America owned the world. Perhaps it did. American Empire had many faces during the Cold War, and thanks to Kinzer, Sidney Gottlieb is one you shouldn’t forget.
Kelley Beaucar Vlahos is executive editor at The American Conservative. Follow her on Twitter @Vlahos_at_TAC